• 简介
• 谷氨酸能三方突触
• 谷氨酸的从头合成途径
• 谷氨酸-谷氨酰胺循环
• 产品
• 参考文献
众所周知,神经元通过突触相互交流。传入的电信号经突触被转换成化学信使,即神经递质。在受到刺激后,神经递质会由传递神经元的突触前释放至突触间隙,然后与接收神经元的突触后受体结合。取决于神经递质的类型,神经元可被刺激或者抑制。目前为止,已有超过100种神经递质被发现,从而使得神经元之间的化学信号具有极大的多样性(Purves et al., 2008)。
在哺乳动物中枢神经系统(CNS)中,谷氨酸是最主要的兴奋性神经递质。据统计估算有超过一半的突触可释放谷氨酸,并且几乎所有中枢神经系统中的兴奋性神经元是谷氨酸能神经元。
星形胶质细胞在谷氨酸能突触中扮演着非常重要的角色(Hertz, 1979, Schousboe et al., 2013 & 2014),1999年,Alfonso Araque (Araque et al., 1999)发现星形胶质细胞是突触的第三个元素。所谓的“三方突触”由突触前及突触后神经末梢和突触周围的星状细胞末端突起(PAP)组成。神经元和星形胶质细胞可被视为一个代谢单元(Squire et al., 2002, Benarroch 2016)。对于谷氨酸能突触,星形胶质细胞可为神经元实现至少两项特别重要的任务:
1. 从突触间隙摄取谷氨酸:谷氨酸受体的过度激活是神经元的兴奋性毒性,也被称为谷氨酸兴奋性毒性。为了避免毒性,星形胶质细胞可以几乎立刻吸收由神经元释放的谷氨酸。
2. 提供谷氨酰胺作为谷氨酸前体:在谷氨酸能神经末梢,星形胶质细胞是维持和调节神经传递所必需的(Perea et al., 2009),并且它控制谷氨酸的生物合成和周转。为此,星形胶质细胞为神经元提供突触惰性前体谷氨酰胺。谷氨酸/谷氨酰胺的合成有两种途径-谷氨酸/谷氨酰胺的从头合成途径(图 1)和谷氨酸/谷氨酰胺的循环(图 2)。
神经元和星形胶质细胞中谷氨酸代谢不平衡也被认为与多种神经系统失调有关(Rudy et al., 2014; Blanco-Suárez et al. 2017; Ferreira et al., 2021; Haroon & Miller 2016)。
谷氨酸是一种非必需氨基酸,它没有穿过血脑屏障,因此在脑中被合成(Purves et al., 2008)。从头合成可能会通过柠檬酸循环(TCA),它不仅仅是生成ATP的一种途径,也为生物合成提供很多中间产物(Berg et al., 2003; Schousboe et al., 2013) (图 1)。例如谷氨酸来源于α酮戊二酸(图1 – 第1步)。从TCA循环中获取的用于神经递质生物合成的中间产物必须及时补充,来确保代谢物的持续可用。在哺乳动物中,草酰乙酸(OAA)可由丙酮酸羧化酶(PC)催化的丙酮酸羧化物补充,该羧化酶仅在星形胶质细胞中表达,而在神经元中不表达(图 1 – 第2步)。因此,神经元自身并不能从头合成谷氨酸(Bak et al., 2006)。这意味着谷氨酸能神经元必须依赖于星形胶质细胞重新补充谷氨酸池进行传递。由于谷氨酸自身具有兴奋性毒性,所以在由星形胶质细胞传送到神经元之前,它会被谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)催化为谷氨酰胺(图1 – 第3、4步)。谷氨酸能神经元可表达谷氨酰胺酶1(GLS1),也被称为PAG (磷酸盐活化的谷氨酰胺酶),该酶可将谷氨酰胺重新转化回为谷氨酸(图1 – 第5步)。
图 1 (可点击产品):发生在星形胶质细胞中的谷氨酸从头合成途径。
(1) 谷氨酸(Glu) 由α酮戊二酸(alpha-KG)生成,它是柠檬酸循环(TCA cycle)的一种中间产物。谷氨酸脱氢酶(GDH) 和天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AAT)可催化α酮戊二酸可逆反应为谷氨酸。(2) 丙酮酸羧化酶(PC)仅在星形胶质细胞中表达,并催化丙酮酸羧化物为草酰乙酸(OAA),来重新补充TCA循环中间产物。(3) 谷氨酸可由谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)转化为谷氨酰胺(Gln)。(4) 谷氨酰胺被传送至神经元。(5)在神经元中,谷氨酰胺由谷氨酰胺酶1(GLS1)催化转化回谷氨酸。
有趣的是,谷氨酰胺的主体部分不是由从头合成途径生成的。定量主导的代谢途径是谷氨酸-谷氨酰胺循环(图2),也被称为谷氨酸-谷氨酰胺穿梭机。这个循环是神经元和星形胶质细胞合作的一个例子,描述了谷氨酸在神经传递中的循环。谷氨酸被释放后,与主要位于突触后膜的谷氨酸受体结合(图2 – 第1步)。谷氨酸受体有两种不同类型,离子通道型受体(AMPAR/GluA, KainateR/GluK, NMDAR/GluN receptors) 和G-蛋白偶联代谢型受体(mGluRs)。为了避免由谷氨酸受体过度活化而导致谷氨酸兴奋性毒性,星形胶质细胞可立即移除经兴奋性氨基酸转运蛋白(EAATs)释放的谷氨酸(Malik & Willnow 2019),转运蛋白主要包括EAAT 1 (又名为GLAST – 谷氨酸-天冬氨酸转运蛋白)和 EAAT 2 (又名为GLT1 -谷氨酸转运蛋白 1) (图2 – 第2步)。还有一小部分谷氨酸可通过EAAT 3 (又名为 EAAC1 – 兴奋性氨基酸载体1)被神经元移除。星形胶质细胞可以由谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)催化,将大部分谷氨酸转化为谷氨酰胺(图2 – 第3步)。然后谷氨酰胺可被钠偶联中性氨基酸转运蛋白(SNATs)运至神经元(图2 – 第4步)。在神经元细胞的线粒体中,谷氨酰胺被谷氨酰胺酶1(GLS1)脱氨转化会谷氨酸(图2 – 第5步)。而再循环的谷氨酸可由囊泡谷氨酸转运蛋白(VGLUTs)转运至突触囊泡,来为下一轮的传递而准备(图2 – 第6步)。
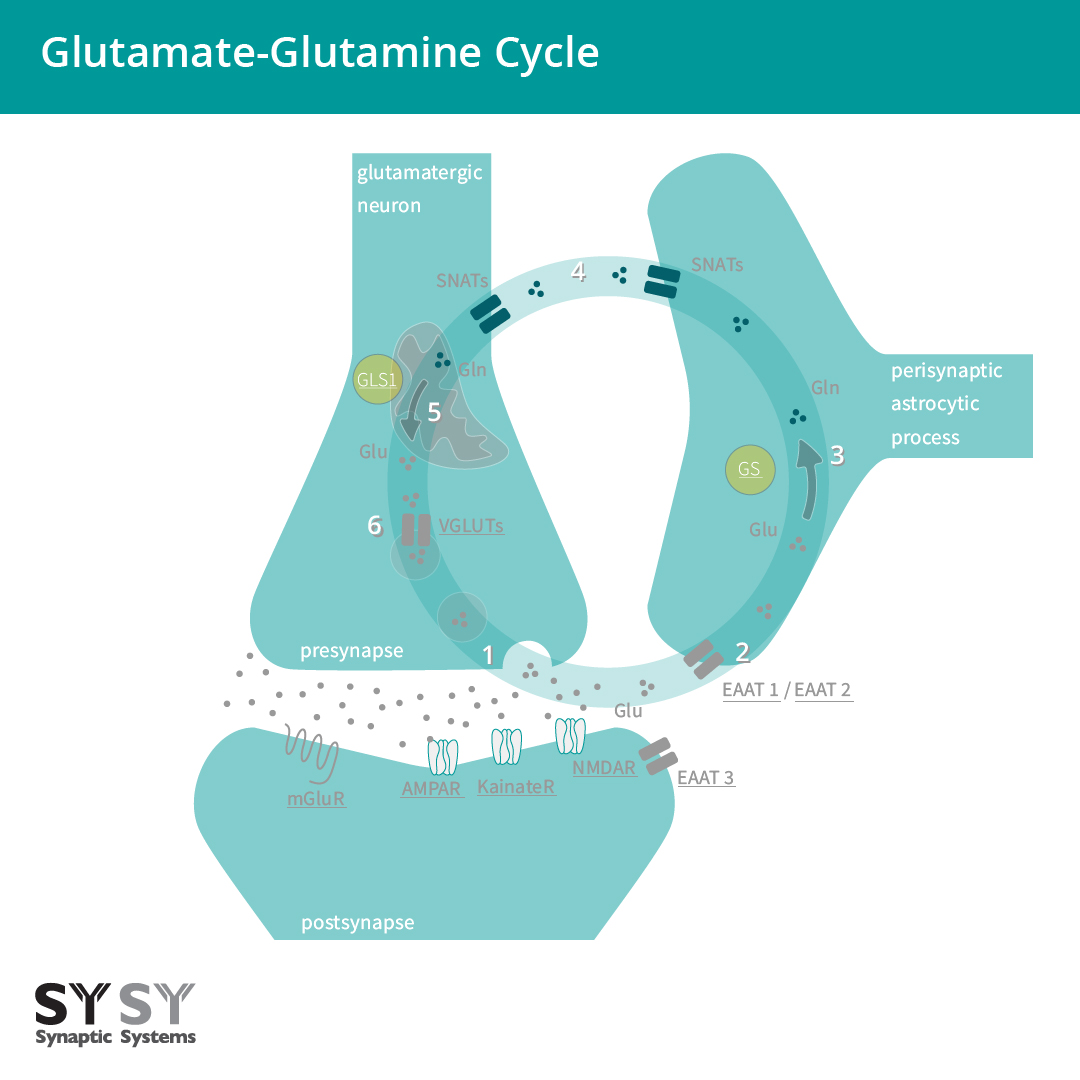
图2 (可点击产品): 谷氨酸能神经元和星形胶质细胞之间的谷氨酸-谷氨酰胺循环。
(1) 谷氨酸(Glu) 被释放后 ,跟离子通道型及代谢型受体结合(AMPAR/GluA、KainateR/GluK、NMDAR/GluN、mGluRs)。(2) 谷氨酸主要由星形胶质细胞通过兴奋性氨基酸转运蛋白EAAT 1/2 移除,部分由神经元通过EAAT 3移除。(3) 星形胶质细胞谷氨酰胺合成酶将谷氨酸(Glu)转化为谷氨酰胺(Gln)。(4) 突触惰性谷氨酰胺被从星形胶质细胞转运至神经元。(5)谷氨酰胺(Gln)由线粒体谷氨酰胺酶1 (GLS1)转化回谷氨酸(Glu)。(6) 谷氨酸被囊泡谷氨酸转运蛋白(VGLUTs)转移至囊泡,为下一轮的传递而准备。
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 182 403 | GluA, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IHC EM | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 182 408 | GluA, rabbit, monoclonal, recombinant IgGrecombinant IgG | ICC | 50 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 182 411 | GluA, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG extracellular | IP ICC | 100 µg | US$425.00 | |
| 182 411C3 | GluA, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG, Sulfo-Cyanine 3 extracellular | ICC | 100 µg | US$470.00 | |
| 182 003 | GluA1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity K.O. | WB IP ICC ExM | 50 µg | US$385.00 | |
| 182 011 | GluA1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG K.O. | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µg | US$435.00 | |
| 182-01P | GluA1, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 182-0P | GluA1, control proteincontrol protein | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 182 103 | GluA2, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IP ICC IHC ExM | 50 µg | US$385.00 | |
| 182 105 | GluA2, Guinea pig, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 50 µg | US$470.00 | |
| 182 111 | GluA2, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG | WB IP ExM Clarity | 100 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 182 113 | GluA2, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IP | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 182 211 | GluA2, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgM IgM | WB | 100 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 182-1P | GluA2, control proteincontrol protein | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 182 203 | GluA3, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IP | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 182-2P | GluA3, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 182 303 | GluA4, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IP | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 182-3P | GluA4, control proteincontrol protein | 100 µg | US$110.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 250 103 | EAAT1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity K.O. extracellular domain | WB | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 250 113 | EAAT1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity K.O. cytoplasmic domain | WB IP ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 250 114 | EAAT1, Guinea pig, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum cytoplasmic domain | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µl | US$370.00 | |
| 250 116 | EAAT1, chicken, polyclonal, IgY fractionIgY fraction cytoplasmic domain | WB ICC IHC | 200 µl | US$365.00 | |
| 250-11P | EAAT1, control peptidecontrol peptide cytoplasmic domain | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 250-1P | EAAT1, control peptidecontrol peptide extracellular domain | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 250 203 | EAAT2, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity K.O. extracellular domain | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 50 µg | US$385.00 | |
| 250 204 | EAAT2, Guinea pig, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum K.O. extracellular domain | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µl | US$370.00 | |
| 250 211 | EAAT2, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG extracellular domain | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 250-2P | EAAT2, control peptidecontrol peptide extracellular domain | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 250 303 | EAAT3, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity currently not available cytoplasmic domain | ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 250 313 | EAAT3, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity cytoplasmic domain | WB | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 250-31P | EAAT3, control peptidecontrol peptide cytoplasmic domain | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 250 403 | EAAT4, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB | 50 µg | US$385.00 | |
| 250 413 | EAAT4, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 50 µg | US$385.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 456 003 | Glutaminase1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 456 004 | Glutaminase1, Guinea pig, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum | WB ICC IHC | 100 µl | US$370.00 | |
| 456-0P | Glutaminase1, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 367 004 | Glutamine synthetase, Guinea pig, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum | WB IHC | 100 µl | US$370.00 | |
| 367 005 | Glutamine synthetase, Guinea pig, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IHC IHC-P | 50 µg | US$470.00 | |
| 367 011 | Glutamine synthetase, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µg | US$420.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 180 313 | GluK1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 180 003 | GluK2, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity K.O. | WB ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 180-0P | GluK2, control proteincontrol protein | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 180 203 | GluK3, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 180 103 | GluK5, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IHC-Fr | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 180-1P | GluK5, control proteincontrol protein | 100 µg | US$110.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 191 002 | mGluR1-α, rabbit, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum | WB | 200 µl | US$360.00 | |
| 191 003 | mGluR1-α, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 50 µg | US$460.00 | |
| 191-0P | mGluR1-α, control proteincontrol protein | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 191 103 | mGluR2, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 191-1P | mGluR2, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 191 508 | mGluR5, rabbit, monoclonal, recombinant IgGrecombinant IgG | IHC IHC-G | 50 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 191 203 | mGluR7b, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$380.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 114 003 | GluN1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity extracellular | WB IP ELISA | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 114 011 | GluN1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG K.O. extracellular | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P IHC-G ExM ELISA | 100 µg | US$435.00 | |
| 114 018 | GluN1, rabbit, monoclonal, recombinant IgGrecombinant IgG extracellular | ICC IHC IHC-G | 50 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 114 103 | GluN1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | ICC IHC IHC-G | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 114-0P | GluN1, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 244 002 | GluN2A/B, rabbit, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum | WB IP | 200 µl | US$360.00 | |
| 244 003 | GluN2A/B, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IP ICC | 50 µg | US$460.00 | |
| 244 004 | GluN2A/B, Guinea pig, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum | WB | 100 µl | US$370.00 | |
| 244-0P | GluN2A/B, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 | ||
| 244 103 | GluN2B, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB IP | 50 µg | US$380.00 | |
| 244 115 | GluN2B, Guinea pig, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity | WB | 50 µg | US$465.00 | |
| 244-1P | GluN2B, control peptidecontrol peptide | 100 µg | US$110.00 |
| Cat. No. | Product Description | Application | Quantity | Price | Cart |
|---|
| 135 011 | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG K.O. | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µg | US$425.00 | |
| 135 011AbOR | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity , AbberiorStar ORANGE | ICC | 100 µg | US$470.00 | |
| 135 011AbRED | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity , AbberiorStar RED | ICC | 100 µg | US$470.00 | |
| 135 011BT | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG, biotin K.O. | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 100 µg | US$475.00 | |
| 135 011C3 | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG, Sulfo-Cyanine 3 K.O. | ICC IHC | 100 µg | US$475.00 | |
| 135 011C5 | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG, Sulfo-Cyanine 5 K.O. | ICC IHC | 100 µg | US$475.00 | |
| 135 302 | VGLUT1, rabbit, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum K.O. | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P ExM | 200 µl | US$365.00 | |
| 135 303 | VGLUT1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity K.O. K.D. | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P IHC-Fr DNA-PAINT Clarity EM ELISA | 50 µg | US$470.00 | |
| 135 303C3 | VGLUT1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity , Sulfo-Cyanine 3 K.O. | ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$500.00 | |
| 135 303C5 | VGLUT1, rabbit, polyclonal, affinity purifiedaffinity , Sulfo-Cyanine 5 K.O. | ICC IHC | 50 µg | US$500.00 | |
| 135 304 | VGLUT1, Guinea pig, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum K.O. discontinued, replacement: 135 318 | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P IHC-Fr ExM Clarity EM FACS | 100 µl | ||
| 135 307 | VGLUT1, goat, polyclonal, antiserumantiserum K.O. | WB IP ICC IHC | 200 µl | US$335.00 | |
| 135 308 | VGLUT1, rabbit, monoclonal, recombinant IgGrecombinant IgG K.O. | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P ExM | 50 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 135 309 | VGLUT1, chicken, monoclonal, recombinant IgYrecombinant IgY K.O. | WB ICC IHC IHC-P | 50 µg | US$420.00 | |
| 135 311 | VGLUT1, mouse, monoclonal, purified IgG IgG K.O. | WB IP ICC IHC IHC-P ELISA | 100 µg | US$425.00 |
Araque et al., 1999: Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. PMID: 10322493
Bak et al., 2006: The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. PMID: 16787421
Benarroch 2016: Astrocyte signaling and synaptic homeostasis. PMID: 27335113
Blanco-Suárez et al. 2017: Role of astrocyte–synapse interactions in CNS disorders. PMID: 27381164
Ferreira et al., 2021: Rutin improves glutamate uptake and inhibits glutamate excitotoxicity in rat brain slices. PMID: 33492574
Haroon & Miller 2016: Inflammation Effects on Brain Glutamate in Depression: Mechanistic Considerations and Treatment Implications. PMID: 27830574
Hertz, 1979: Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes I. Turnover and metabolism of putative amino acid transmitters. PMID: 42117
Malik & Willnow 2019: Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters in Physiology and Disorders of the Central Nervous System. PMID: 31726793
Perea et al., 2009: Tripartite synapses: astrocytes process and control synaptic information. PMID: 19615761
Rudy et al., 2014: The Role of the Tripartite Glutamatergic Synapse in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s Disease. PMID: 25821641
Schousboe et al., 2013: Astrocytic Control of Biosynthesis and Turnover of the Neurotransmitters Glutamate and GABA. PMID: 23966981
Schousboe et al., 2014: Glutamate Metabolism in the Brain Focusing on Astrocytes. PMID: 25236722
Squire et al., 2002: Fundamental Neuroscience, 2nd Edition, ISBN: 9780080521800
Purves et al., 2008: Neuroscience, 4th Edition, ISBN: 9780878936977
Berg et al., 2002: Biochemistry, 5th Edition, ISBN: 9780716746843